The 2024 election is consequential for LGBTQ people and our equality. LGBTQ voters are poised again to be the decisive edge in close-contest states in the presidential race as well as the elections that will determine the balance of power in the U.S. Senate and U.S. House of Representatives.
But it’s not just about choosing candidates. Here are issues and proposals up for a vote that will have an impact on the LGBTQ community, including in the battleground states and states that have passed legislation targeting LGBTQ people.
Reproductive Health Care
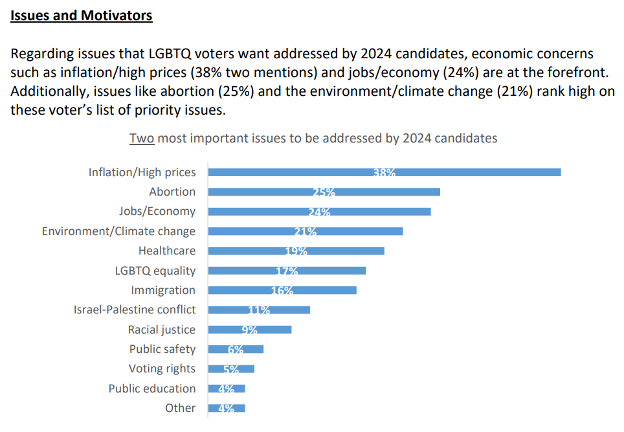
According to the results of a GLAAD and Pathfinder poll released earlier this year, abortion is the second most important issue for LGBTQ voters in the 2024 election. LGBTQ people can and do get pregnant and need reproductive health care. Many of the same states with abortion bans also have enacted bans and restrictions on transgender health care.
Ten states have ballot initiatives to protect access to abortion, including the battlegrounds of Arizona and Nevada, as well as Colorado, Florida, Maryland, and New York. Nebraska has competing ballot initiatives – one expanding access to abortion, one restricting it to the first trimester of pregnancy. Since the Dobbs decision, voters in every state with ballot initiatives have passed expanded protections and access to reproductive care – eight elections and counting.
Arizona
Proposition 139: Amend the state constitution to define as fundamental the right to abortion “through fetal viability,” or about 24 weeks. Current law allows for abortions “until 15 weeks of pregnancy.” In April, the Arizona Supreme Court ruled 4-2 to uphold an 1864 law “prohibiting abortion in most circumstances except to save the life of the mother.” The following month, Arizona Gov. Katie Hobbs cast her signature to revoke the law.
“This election is more than a presidential election. In Arizona, like many states, the outcomes of these ballot initiatives could drastically change rights and freedoms granted to individuals in our state including the quality and availability of reproductive health care for Arizona families,” said Michael Soto, president of Equality Arizona.
“Make sure you don’t forget to vote on the ballot initiatives like Prop 139, in fact the most effective way to vote this year in Arizona is to start with the propositions and work your way up to the presidential race. Our rights and freedoms are on the line, and your vote will matter more than it ever has in this election.”
Arizona’s U.S. Senate race features Rep. Ruben Gallego and former gubernatorial candidate Kari Lake. Lake has promised to make Arizona a “sanctuary state” for the unborn, called abortion the “ultimate sin” and endorsed a federal ban on abortion before flipping support. Rep. Gallego supports Prop 139 and “restoring abortion access” in Arizona.
GLAAD has documented the LGBTQ records of Gallego and Lake.
Colorado
Amendment 79: Protect Coloradans’ right to abortion and prevent governmental interference, denial, or discrimination. Allow for Medicare and other state-funded insurance to “cover abortion services.” As a constitutional amendment, this proposal requires at least 55% voter approval to pass.
Florida
Amendment 4: Add abortion protections to the Florida Constitution’s Declaration of Rights. A “yes” vote would enshrine abortion protections “before viability” or to protect the health of the patient. Unchanged will be a current provision requiring parents “to be notified before a minor can receive an abortion.” Recent polling shows 76% of voters expressed support for the proposal. Florida currently has a ban on abortions after six weeks of pregnancy, one of the strictest bans in the country, as well as a ban on health care for transgender people, which can currently be enforced as the law is appealed.
Florida’s incumbent Sen. Rick Scott is running for re-election to the U.S. Senate. Scott has backed Florida-based anti-LGBTQ extremist book banning group Moms for Liberty, and opposes Florida’s Amendment 4.
In recent years, The Hill reports, Floridians passed amendments restoring voting rights to felons who have served their time, voted to increase the minimum wage, and legalized medicinal marijuana.
Illinois
Assisted Reproductive Healthcare Advisory Question: Gauge public opinion and advise state officials on whether health insurance plans in Illinois should be required “to provide for medically assisted reproductive treatments, including in vitro fertilization.”
In 2023, Illinois’ legislature passed, and Gov. J.B. Pritzker signed into law, a bill enshrining the right to abortion and maternity care. The bill was sponsored by out state Rep. Kelly Cassidy, who said: “While all around us opponents are using misinformation and misogyny to justify attacks on bodily autonomy, I’m proud that here in Illinois, we’ve declared unequivocally that we trust patients and doctors to make these decisions safely and privately.”
Maryland
Question 1: Enshrine reproductive freedom rights within the Maryland Constitution’s Declaration of Rights. The right to reproductive freedom includes, “the ability to make and effectuate decisions to prevent, continue, or end one’s own pregnancy.” A simple majority is needed for the measure to pass.
Maryland’s race for U.S. Senate includes former Gov. Larry Hogan, who vetoed a bill to expand access to abortion in 2022. His opponent, Prince George’s County Chief Executive Angela Alsobrooks, said Hogan would be the “51st vote” swinging the Senate majority to the party that would not vote to restore the rights of Roe nationwide.
Alsobrooks told the Associated Press “there will never be a vote as to whether or not we should codify Roe in federal law if the Republicans are in the majority… they have made it clear, they’ve essentially declared war on reproductive freedoms, and we know that that vote would never happen.”
Missouri
Amendment 3: Enshrine reproductive freedom rights, including “prenatal care, childbirth, postpartum care, birth control, abortion care, miscarriage care, and respectful birthing conditions” into the state constitution through an amendment. Previously threatened with removal from the November ballot, the Supreme Court of Missouri “reversed a lower court ruling against the measure.”
Incumbent Sen. Josh Hawley, who is running for re-election this year, lied about Amendment 3 while also attacking essential health care for transgender people that’s supported by every major medical association.
“Hawley’s fear mongering on trans health care for youth referenced practices that are already largely restricted in Missouri,” St. Louis Public Radio reported. “In 2023, the state passed a sweeping ban on gender-affirming care for minors.”
Supporters of Amendment 3, including the ACLU and Hawley’s Senate race opponent, Lucas Kunce, called Hawley’s remarks false, outlandish, and an attempt to distract voters, KSMU reports.
Hawley’s LGBTQ record is documented on the GLAAD Accountability Project. Hawley is among five senators who voted to object to the Electoral College counts showing Donald Trump lost the 2020 election, casting their votes hours after the deadly insurrection at the United States Capitol. Hawley went on to co-sponsor a bill targeting transgender students. The five senators voting to protect Trump’s lie, then targeting transgender youth, are Sen. Tommy Tuberville of Alabama, Sen. Josh Hawley of Missouri, Sen. Cindy Hyde-Smith of Mississippi, Sen. Roger Marshall of Kansas, and Sen. Ted Cruz of Texas.
Montana
CI-128: Amend the state constitution to enshrine reproductive rights, “including the right to abortion,” and to “travel for medical services” without government interference “up until the point of fetal viability.”
Montana’s race for U.S. Senate is among those that will determine whether the Senate remains in the control of the pro-equality majority.
In a September 30 debate, incumbent Sen. Jon Tester supported the ballot measure and a person’s fundamental right to make private health care decisions: “I believe women should be able to make their own health care decisions. That’s the bottom line. It shouldn’t be the federal government. It shouldn’t be a bureaucrat. It shouldn’t be a judge,” Tester said. Tester also supports federal legislation to protect abortion access before fetal viability — generally considered to be around 24 weeks, according to Montana Public Radio.
U.S. Senate candidate Tim Sheehy is anti-abortion and calls Tester’s stance extreme. Sheehy has said “I am proudly pro-life.”
Nevada
Question 6: The Right to Abortion Initiative. A “yes” vote supports providing for a state constitutional right to an abortion.
“Abortions in Nevada are currently legal up to 24 weeks after the start of pregnancy and after 24 weeks if a physician believes the pregnant person’s life or health is at risk,” the Nevada Current reports
“Those protections were put in place via a citizen-driven referendum passed by voters in 1990 and would require a direct vote of the people to change. Question 6 would establish abortion as a fundamental right in the state constitution, which also requires a vote of the people to amend.”
“This doubles down on the protections on statute,” Lindsey Harmon, president of Nevadans for Reproductive Freedom told the Current. “It makes it twice as hard to repeal or amend the referendum.”
Incumbent Sen. Jacky Rosen is running for her second term in the Senate and supports Question 6. Her opponent, retired Army Capt. Sam Brown has said he is “pro-life,” that he’s “not for changing existing law,” and in 2022 told the Reno Gazette-Journal that he will “continue to protect life by voting against any federal funding of abortion and by voting to confirm justices who protect life.”
GLAAD has documented the LGBTQ records of Rosen and Brown, here.
Marriage Equality
The Supreme Court’s 2022 ruling overturning Roe v. Wade revealed that marriage equality under Obergefell v. Hodges is far from safe. And while the Respect for Marriage Act would protect same-sex marriages that have already taken place legally, it does not “prevent states from refusing to license the unions.” In order to enshrine these rights, the following states have proposed legislation that would protect marriage equality:
California
Proposition 3: Repeal the now infamous Proposition 8, a 2008 ballot initiative defining “marriage as a union between one man and one woman.” A “yes” vote would establish as fundamental the right to marry. Prop 8 was overturned in the U.S. Supreme Court case Hollingsworth v. Perry, in 2013.

“Here in California, we believe the ability to marry the person you love, regardless of race, ethnicity, gender, or sexual orientation, is a fundamental right,” said State Sen. Toni Atkins. “During a time when our civil rights are under attack by courts and state houses across the nation, we cannot afford to wait to enshrine marriage equality in California’s Constitution – the time to act is now.”
Colorado
Amendment J: Remove the ban on same-sex marriage in the Colorado Constitution. Currently, the state constitution still defines marriage as “only a union of one man and one woman,” wording that was nullified with the U.S. Supreme Court’s 2015 Obergefell decision. Justice Clarence Thomas has called on Obergefell to be “reconsidered” in his concurrence overthrowing Roe.
“Marriage has been many things throughout history, but for queer people, it’s always been about more than just a legal union—it’s been a defiant act of love and resistance.” said Jax Gonzalez, political director at One Colorado, the state’s leading LGBTQ advocacy organization.
“The Obergefell decision was a monumental step forward, but with the fall of Roe, we know we can’t rely on Supreme Court precedent to protect the freedom to marry. Removing the ban on same-sex marriage from the Colorado Constitution isn’t just about love or legal protection—it’s about affirming that our love, our dignity, and our equality are not up for debate. We owe it to the generations who fought before us, and to the future we’re building, to ensure these rights are secure.”
Of particular note: One Colorado reported that no-anti transgender initiatives made it to the November ballot. This comes after an anti-LGBTQ political action committee announced in August that they failed to collect enough signatures to advance anti-transgender legislation onto the 2024 ballot.
Hawaii
Remove Legislature Authority to Limit Marriage to Opposite-Sex Couples Amendment: Amend the state constitution to protect same-sex marriage. A current constitutional provision gives the legislature “the power to reserve marriage to opposite-sex couples.”
Voting Rights
According to a report by The Williams Institute, more than 210,000 transgender adults could “face barriers to voting this fall” because their forms of identification don’t match their gender. State agencies in Missouri and Texas have removed protocols for trans people to correct their birth certificates. Ballot measures this year are targeting ways candidates appear on the ballot and can campaign.
Among the higher profile state ballot initiatives is Ohio’s Issue 1, which aims to fix the current manipulation of maps designed to favor one party over another (gerrymandering).
Ohio Issue 1: Establish a 15-member Ohio Citizens Redistricting Commission composed of five each of Democrats, Republicans, and Independents. Currently, the redistricting commission is comprised of politicians. Issue 1 would mandate politicians be excluded, along with lobbyists and political consultants.
Equality Ohio explained the measure to its followers on TikTok and Instagram: “Gerrymandering leads to extreme legislation—it hurts LGBTQ+ Ohioans, period.”
Gerrymandered maps have helped create an extremist supermajority in the Ohio state legislature that last year passed a combination bill banning medically necessary health care for transgender youth and banning trans youth from school sports. Ohio has successfully worked around the gerrymandered supermajority with ballot measures, including two measures that helped codify the right to reproductive health care last year.
In August 2023, Ohio voters passed a ballot measure that protected a majority vote for ballot measures, then in November 2023, voters passed an amendment to add abortion rights to the state constitution, with robust voter turnout for an off-year election. Extremist lawmakers opposed both measures.
Signal Cleveland spelled out the stakes of Issue 1: “Under the current maps, Republicans hold about 66% of Ohio’s congressional and state legislative seats – giving them a veto-proof majority in the General Assembly – although their share of the vote is closer to 56%.”
If Ohio voters pass Issue 1, the state would join Michigan and Wisconsin, which have successfully broken down partisan gerrymandering, ensuring accurate representation in the state’s voting districts.
Additional states with measures about voting procedures and methods include:
Arizona
Proposition 133: Update the state constitution to “require partisan primary elections for partisan offices,” thus preventing all candidates from running in the same primary. Under the proposed amendment, political parties would nominate their own candidates to open positions, as has already been the practice.
Proposition 134: Establish within the state constitution an amendment requiring citizens pursuing a ballot measure to gather a percentage of signatures from every legislative district; 10% for statutory amendments and 15% for statewide initiatives.
Proposition 137: Replace term limits for state Supreme Court justices and superior court judges with “terms of good behavior.” If passed, this proposal would strip voters of the right to decide whether or not to retain state Supreme Court justices. “Any justices on the November ballot would also automatically stay in office if the measure passes, even if voters choose to reject them.”
Proposition 140: Create open primary elections, requiring “all candidates for a specific office,” regardless of political affiliation, to “run against each other in a single primary election.” Lawmakers would then have the option to establish “a top-two general election featuring the top primary candidates,” or a ranked-choice voting system in the general elections “featuring the top primary candidates.”
Colorado
Proposition 131 (Initiative 310): Eliminate partisan primaries and place all qualified candidates “on the same primary ballot.” The four candidates with the top number of votes would move on to the November general election, which would ask voters to rank them based on their “order of preference.”
Florida
Amendment 1: Require school board candidates to list their party affiliation on the ballot, starting with the November 2026 general election.
Illinois
Penalties for Candidate Interference with Election Worker’s Duties Advisory Question: Asks voters if candidates who interfere with the official duties of election workers should be subject to civil penalties. This is a non-binding advisory question, and will be used to advise state officials.
Iowa
Iowa Require Citizenship to Vote in Elections and Allow 17-Year-Olds to Vote in Primaries Amendment: Prohibits noncitizens from voting by amending the state constitution to read that “only” U.S. citizens can vote, rather than “every” U.S. citizen. In addition, the proposal would permit “17-year-olds to vote in party primary elections, so long as they turn 18 by the general election.”
Missouri
Amendment 7: Amend the state constitution to limit voting to U.S. citizens who are 18 years of age or older. In addition, the proposal would “prohibit the ranking of candidates by limiting voters to a single vote per candidate or issue,” and advance one winner from the primary elections to the general election.
Montana
CI-126 and CI-127: CI-126 would create ranked-choice primaries for candidates running for “governor, lieutenant governor, state executives, state legislators, and congressional offices.” Following the election, the top-four candidates would advance to the general election, “regardless of party.” Meanwhile, CI-127 would require candidates for the following offices to win a majority of the vote, rather than a plurality, in order to secure the election: “governor, lieutenant governor, secretary of state, auditor, attorney general, superintendent of public instruction, state legislature, and congressional offices.”
Wisconsin
Citizenship Voting Requirement Amendment: Amends the state constitution to stipulate “that only U.S. citizens who are 18 years old or older can vote in federal, state, local, or school elections.” Current language states “every” U.S. citizen can vote, but the proposal would change this to “only.” If passed, the measure would capitalize on fear mongering about noncitizen voting, “but noncitizens cannot legally use their IDs or licenses to register and vote.”
Earlier this year, Wisconsin Gov. Tony Evers signed new legislative maps into law, creating better balance within Assembly districts.

To learn more about statewide initiatives that will appear on your ballot, we recommend familiarizing yourself with them through nonpartisan sites like Ballotpedia (also linked from the title of each ballot proposal).













